Understanding Electrical Alternating Current
Introduction:
Have you ever wondered how electricity flows through our homes and powers our devices? Electrical alternating current, also known as AC, plays a vital role in this process In this article, we will explore the ins and outs of AC power and its applications. AC was championed by renowned inventor Nikola Tesla in the late 19th century, who demonstrated its advantages over DC.
Over time, AC became the standard for electrical power transmission due to its ability to easily transform voltage levels and travel long distances efficiently.
What is Alternating Current?
Electrical alternating current is a type of electrical current where the flow of electric charge periodically reverses direction. This differs from direct current (DC), where the charge flows in one direction. AC is the most common form of electricity used in households and businesses worldwide. It is generated by power stations, transmitted over long distances, and ultimately used to power various devices. and most commonly used form of electricity in households and commercial buildings, delivering power through electrical grids.
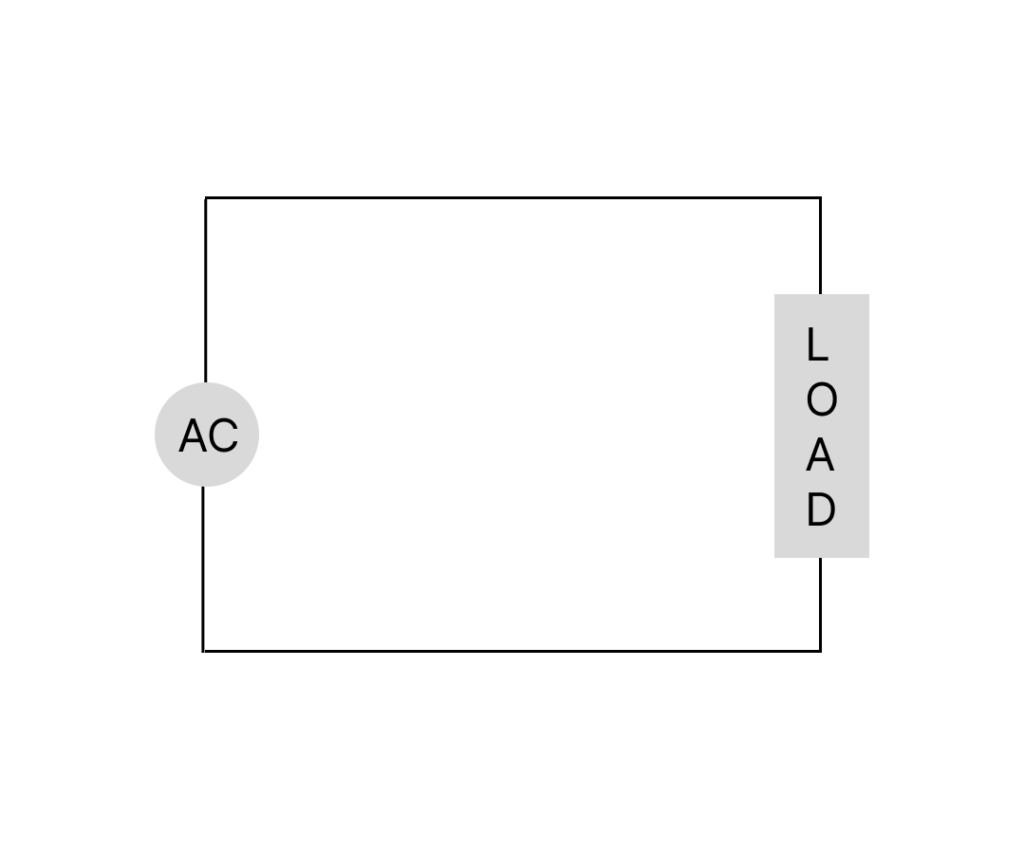
How AC Works:
Importance of AC Current:
Power Distribution
AC current is used for power distribution in electrical grids (transformers) worldwide, enabling electricity to reach homes, businesses, and industries with minimal loss.
The ability to step up or step down voltage levels using transformers makes ac current ideal for long-distance transmission.
Versatility and Efficiency
AC current is versatile and can power a wide range of devices, from small appliances to large machinery.
The ability to easily convert AC to DC using rectifiers allows for efficient operation of electronics and power tools.
Safety Considerations
AC current is generally considered safer than dc current for high-power applications, as it can be easily controlled and isolated in case of electrical faults.
Standardized voltage levels for ac power distribution ensure uniform safety measures across different locations.
Applications of AC Power:
AC power is versatile and used in a wide range of applications, including
Conclusion:
In conclusion, electrical alternating current is a key component of our electrical systems, powering everything from our homes to industrial machinery and transportation networks. Understanding how AC works and its applications can provide valuable insight into the technology that surrounds us daily. Next time you turn on a light or charge your phone, remember the role of AC power in making it all possible.
Remember to stay safe and always consult a professional for any electrical work in your home or workplace.
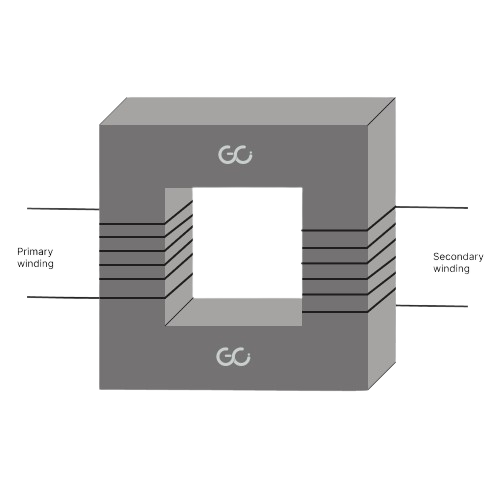
What is transformer? – Working principle, Construction, and Types
4.89 rating on Google
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is the Advantages of AC current?
AC current offers several advantages over DC, including:
1) Efficient transmission over long distances.
2) Ability to step up voltage or step down voltage using transformers.
3) Compatibility with various types of devices and equipment
What is the definition of AC current?

Electrical alternating current is a type of electrical current where the flow of electric charge periodically reverses direction. This differs from direct current (DC), where the charge flows in one direction. It is generated by power stations, transmitted over long distances, and ultimately used to power various devices.
thank you for visiting
Alternating Current- definition, Working, Importance, advantages, application, Safety Considerations in easy language.
Best information sir thanks you so much