Electric transformers are essential components of our electrical system, playing a crucial role in transmitting power efficiently and safely. In this article, we will delve into the intricate workings of electric transformers, explaining their purpose, construction, and functionality in detail
4.89 rating on Google

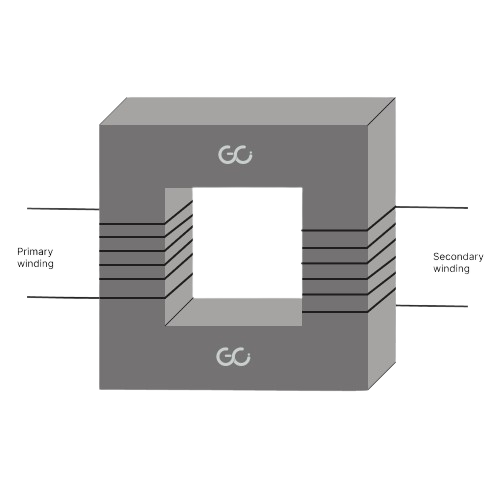
Transformer construction:
Steps in the Operation :
in simple language
Working principle of transformer?
The operation of an electric transformer is based on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. When an alternating current (AC) flows through the primary coil, it generates a changing magnetic field around the core. This changing magnetic field induces a voltage in the secondary coil, producing an output current for the load
They help in:
besic
What are the types of transformers?
Other types :
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common loss occur in transformers?
Copper Losses:- The resistance of the copper windings leads to energy losses in the form of heat.
Iron Losses:- Hysteresis and eddy current losses occur in the core material.
Why is transformer maintenance important?

Proper maintenance and safety protocols are essential to ensure the longevity and efficiency of electric transformers. Regular inspections, oil level checks, and thermal monitoring play a vital role in preventing malfunctions and hazards.
What are some important safety tips for transformers?

Keep the area around the transformer clear of obstructions.
Regularly monitor oil levels and temperatures.
Implement a robust maintenance schedule to detect potential issues early.
What factors determine the efficiency of a transformer?

The efficiency of a transformer is influenced by factors such as core material, winding design, operating temperature, and load conditions.
How do you determine the appropriate size for an electrical transformer for a specific application?

Transformer sizing depends on factors like the load demand, maximum demand, voltage requirements, and environmental conditions of the application.
what are the Benefits of Electrical Transformers?

Electrical transformers offer numerous benefits, including:
Efficient power distribution
Voltage regulation
Isolation between circuits for safety
Reduced energy loss during transmission
What are the basic components of an electrical transformer?

An electrical transformer consists of primary and secondary windings, a magnetic core, and insulation materials that ensure safety and efficiency.
Conclusion:
Electric transformers are indispensable devices that facilitate the efficient and safe transmission of electrical energy. By understanding how they work and their significance in the power distribution network, we can appreciate the vital role they play in our everyday lives. Next time you turn on a light or charge your electronic device, remember the silent yet powerful operation of electric transformers behind the scenes
Thank you For visiting
Transformer Working principle, Construction, Operation, Advantages, Types, specific application, losses, maintenance, efficiency, and important safety tips.
Working Principle

An electric transformer is based on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. When an alternating current (AC) flows through the primary coil, it generates a changing magnetic field around the core. This changing magnetic field induces a voltage in the secondary coil, producing an output current for the load.

Step-Up, Step-Down, Isolation Transformers and other like, Auto-Transformer, Distribution Power Transformer with detailed explanation.
What are the most common loss occur in transformers?
Copper Losses:- The resistance of the copper windings leads to energy losses in the form of heat.
Iron Losses:- Hysteresis and eddy current losses occur in the core material.